6.1 Injuries
Exposure to chemical and physical hazards may cause:
- Burns
- Corrosive injuries
- Eye injuries
- Poisoning via skin contact, inhalation or ingestion
Heat burn
Burns are categorized in three classes, illustrated below.
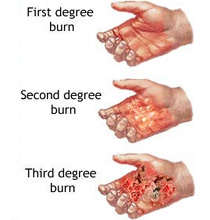
First degree burn affects the top layer of the skin. Symptom of the first degree burn is red, non-blistered skin.
Second degree burn affects the epidermis and dermis. Causes pain, redness, swelling and blistering.
Third degree burn goes through the dermis and affect deeper tissues. It results in white or blackened, charred skin that may be numb.
In the case of a first or second degree burn:
- Rinse with plenty water for at least 15 minutes.
- Seek medical advice if necessary.
- Cover with sterile, non-adhesive bandage or clean cloth.
- Do not remove clothing covering the burn.
In the case of a third degree burn:
- Do not rinse with water.
- Seek medical attention or call emergency number 112 for an ambulance.
- Prevent shock.
- Do not remove clothing covering the burn.
- If possible cover the burned area with a clean and dry piece of fabric.
Always seek medical advice for a burn if:
- The burn involves face, hands, feet, genitals or joint
- It is caused by chemicals or electricity
- The burn is larger than your hand
- Second or third degree burns
Emergency shower and eyewash station

Use the yellow handle with arrow to start the emergency shower. There is one handle for standing up and one close to the floor.
Cold burn
- Dry ice (-78 °C)
- Liquid nitrogen (-196 °C)
Treat as heat burn.
Chemical burn/Corrosive injuries
A chemical burn occurs when living tissues is exposed to corrosive substances such as strong acid or base.
In case of contact, immedietly flush the effected area with plenty of water:
- Acids - rinse with water
- Bases - rinse with water until the skin does not feel oily
Corrosive injuries, treat as heat burn.
